How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial imagery. We’ll cover everything from understanding drone controls and navigation to troubleshooting common issues and adhering to legal and ethical considerations. Whether you’re a novice or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the various types of drones and controllers available, guiding you through the process of calibration, flight mode selection, and camera operation. This guide also emphasizes the importance of adhering to all applicable laws and regulations, ensuring you operate your drone safely and ethically. By the end, you’ll possess a thorough understanding of how to operate a drone, allowing you to capture breathtaking aerial perspectives with confidence and expertise.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring both safety and operational efficiency. This involves a meticulous inspection of the drone itself, a thorough understanding of the surrounding environment and applicable regulations, and preparation for potential contingencies.
Drone Inspection
A thorough pre-flight inspection minimizes the risk of malfunctions during flight. This involves checking the drone’s physical condition, its components, and its systems.
| Check Item | Pass/Fail Criteria | Check Item | Pass/Fail Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | All propellers are securely attached and undamaged. | Camera | Camera lens is clean and free of obstructions; gimbal moves smoothly. |
| Battery | Battery is fully charged and securely connected; no visible damage. | GPS Signal | Sufficient satellites acquired (typically 6+). |
| Motor Arms | No visible damage or looseness; motors spin freely. | Body | No cracks, damage, or loose parts on the drone body. |
| Sensors | All sensors (e.g., IMU, barometer) are functioning correctly. | Communication System | Strong signal between the drone and controller. |
Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Familiarizing yourself with local drone regulations and airspace restrictions is non-negotiable. Websites such as the FAA’s B4UFLY app (in the US) or similar national aviation authorities provide essential information on designated flight zones, no-fly zones, and required permissions.
Battery and Propeller Safety Check
Battery safety is paramount. Always inspect the battery for any signs of damage (swelling, cracks, leaks). Ensure the battery is properly connected and firmly seated in the drone. Similarly, carefully examine propellers for any cracks, chips, or damage. Replace any damaged components immediately.
Pre-Flight Checklist
A comprehensive checklist aids in consistent pre-flight preparation. This checklist should include weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation), emergency procedures (communication plan, designated landing area), battery charge level, and a visual inspection of the drone and surrounding area for obstacles.
- Check weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation)
- Inspect drone for physical damage
- Verify battery charge level
- Confirm GPS signal acquisition
- Review planned flight path and potential hazards
- Establish communication plan in case of emergency
- Identify designated emergency landing area
Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding drone controls and navigation is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different controllers offer varying functionalities, and mastering flight modes is crucial for achieving precise control and stability.
Drone Controller Types and Functionalities
Several types of drone controllers exist, each with unique features and capabilities. The choice often depends on the drone model and the user’s experience level.
- Standard Gamepad-Style Controller: Intuitive joystick controls for altitude, direction, and speed. Typically includes buttons for camera control and flight mode selection.
- Smartphone/Tablet Controller: Utilizes a mobile device as the interface, providing a visual representation of the drone’s position and telemetry data. Often features advanced camera controls and flight planning capabilities.
- Professional Controllers: Offer advanced features such as customizable control mappings, integrated telemetry displays, and support for multiple drones.
Compass and GPS Calibration

Accurate compass and GPS calibration are vital for stable flight. The process typically involves performing a series of movements as instructed by the drone’s software, ensuring the drone correctly orients itself to its surroundings and receives a clear GPS signal.
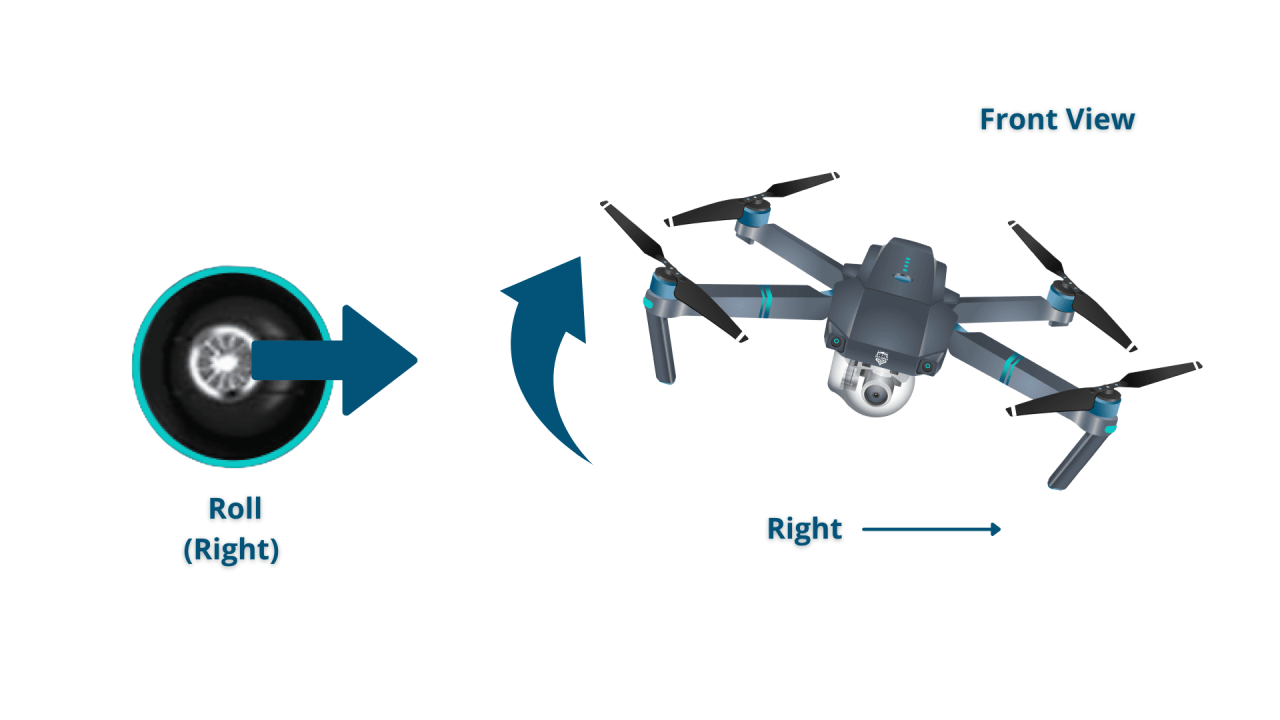
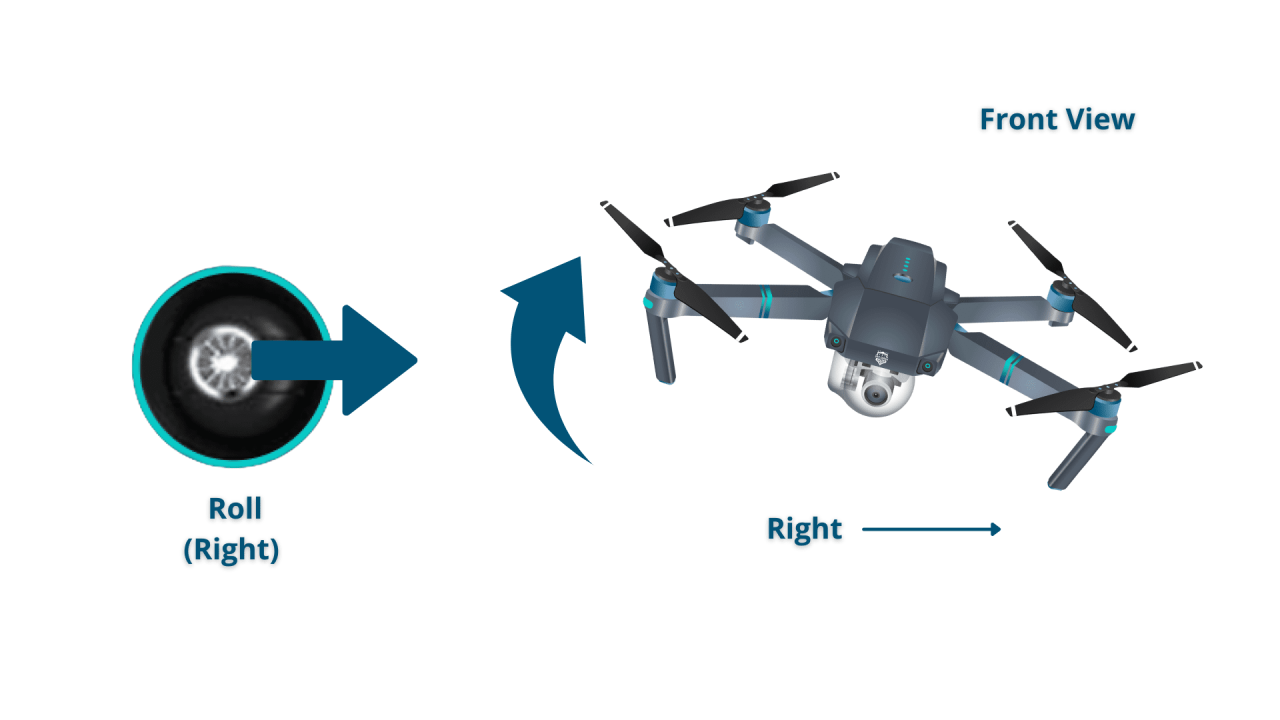
Controlling Altitude, Direction, and Speed
Most controllers use joysticks for controlling altitude (vertical movement), direction (yaw, pitch, roll), and speed. The specific control mappings vary depending on the drone model and controller type, but generally, one joystick manages vertical and lateral movement, while the other controls the drone’s rotation.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of autonomy and control. Understanding their applications is essential for safe and effective drone operation.
- GPS Mode: The drone maintains its position using GPS data, making it ideal for stable hovering and precise movements.
- Attitude Mode: The drone’s orientation is maintained relative to its initial position, useful for acrobatic maneuvers but requiring more skill.
- Sport Mode (or similar): Often allows for faster and more agile flight, but requires greater skill and careful attention to safety.
Taking Off and Landing: How To Operate A Drone
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are critical aspects of drone operation. Following established procedures minimizes the risk of accidents and ensures the longevity of your drone.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
Before takeoff, ensure the drone is calibrated, the battery is fully charged, and the area is clear of obstacles. Perform a pre-flight check, and then initiate takeoff slowly and steadily, monitoring the drone’s altitude and stability.
Smooth Landing Procedure
Approach the landing area slowly and steadily, reducing altitude gradually. Maintain a stable hover before gently lowering the drone to the ground. Once landed, switch off the drone and remove the battery.
Emergency Landing Situations and Responses
Situations requiring emergency landings include low battery warnings, loss of GPS signal, or unexpected malfunctions. In such scenarios, prioritize a safe landing in a clear area, assessing the situation and taking necessary precautions.
Pre-Flight and Post-Flight Procedures
- Pre-flight checks (battery, propellers, GPS signal)
- Calibration (compass, GPS)
- Check surroundings for obstacles and people
- Takeoff
- Flight
- Landing
- Post-flight checks (battery, propellers)
- Drone storage
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The drone’s camera capabilities are a key selling point. Mastering camera settings and techniques enhances the quality of your aerial photography and videography.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Understanding ISO, shutter speed, and aperture allows you to optimize image quality in different lighting conditions. Higher ISO values are useful in low light, but can introduce noise. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur. Aperture controls depth of field, influencing the focus area.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Achieving high-quality aerial shots involves considering composition, lighting, and camera movement. Plan your shots carefully, utilizing the drone’s various flight modes for smooth and controlled movements.
Camera Angles and Perspectives
Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives to capture unique and compelling visuals. Overhead shots provide a bird’s-eye view, while low-angle shots emphasize scale and perspective.
Understanding Camera Features
Familiarize yourself with the drone’s camera features, including zoom capabilities, image stabilization, and video recording settings. Understanding these features allows you to maximize the creative potential of your drone.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with careful preparation, drone malfunctions can occur. Knowing how to troubleshoot common issues ensures efficient problem-solving and minimizes downtime.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
| Malfunction | Potential Cause | Malfunction | Potential Cause |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption | GPS Signal Loss | Poor satellite reception, interference |
| Motor Failure | Motor damage, loose connections, overheating | Gimbal Malfunction | Mechanical failure, software glitch |
| Controller Disconnection | Low battery in controller, interference | Sudden Drop in Altitude | Barometer malfunction, GPS signal loss |
Troubleshooting Steps

Troubleshooting involves systematic checks and adjustments. Start with simple solutions like checking battery levels and signal strength, before proceeding to more complex issues.
Drone Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are essential for optimal performance and longevity. This includes inspecting the drone for damage, cleaning propellers and sensors, and lubricating moving parts.
Troubleshooting Signal Loss
A flowchart can aid in systematically troubleshooting signal loss. The flowchart would guide the user through steps like checking controller battery, drone battery, radio interference, and distance from the drone.
Drone Flight Practice and Skill Development
Consistent practice is key to mastering drone piloting skills. Starting with basic maneuvers in a safe environment and gradually progressing to more advanced techniques builds confidence and proficiency.
Practicing Basic Drone Maneuvers
Begin by practicing basic maneuvers such as hovering, controlled ascents and descents, and directional movements in a spacious, open area free from obstacles. Gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers as your skills improve.
Importance of Practice Environment
A spacious, open area is crucial for safe practice. Avoid practicing near obstacles, people, or buildings. Select a location with minimal wind and good visibility.
Training Plan for Skill Progression
A structured training plan allows for progressive skill development. Begin with basic hovering and control, then move to more complex maneuvers such as figure-eights, and finally, incorporate camera operation into your practice sessions.
Practicing in Various Weather Conditions
Practicing in various weather conditions (within safe limits) helps build experience and confidence. Start with calm conditions, then gradually progress to slightly windier conditions, always prioritizing safety.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Responsible drone operation involves adhering to all applicable laws and regulations, as well as ethical considerations regarding privacy and respecting others’ property.
Adhering to Laws and Regulations, How to operate a drone
Understanding and complying with local drone laws and regulations is crucial to avoid legal consequences. This includes registering your drone, obtaining necessary permits, and respecting airspace restrictions.
Ethical Considerations in Drone Photography and Videography
Ethical considerations encompass respecting privacy, obtaining consent when necessary, and avoiding intrusive or harmful actions. Avoid filming individuals without their consent, and always respect private property.
Legally Restricted Drone Operation
Several situations might legally restrict drone operation, including flying near airports, critical infrastructure, or during emergencies. Always check local regulations before flying.
Responsible Drone Use
Responsible drone use contributes to a safe and enjoyable environment for everyone. Avoid reckless flying, respect airspace restrictions, and be mindful of the impact of your drone operations on others.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundation in safe and responsible drone piloting, covering pre-flight procedures, flight controls, camera operation, troubleshooting, and legal considerations. Remember that consistent practice in a safe environment is key to developing your skills. As you gain experience, explore advanced techniques and always prioritize safety and ethical considerations.
The skies await – fly responsibly and enjoy the breathtaking perspectives that drone technology offers.
FAQ
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with obstacle avoidance and return-to-home functionality.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful planning and practice, and a great resource to help you learn is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, ensuring you’re well-prepared for safe and effective drone operation.
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time per battery charge.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires practice and knowledge, and a great resource for learning is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Ultimately, safe and effective drone operation hinges on consistent practice and adherence to safety protocols.
What happens if I lose signal with my drone?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically guides the drone back to its takeoff point if signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight whenever possible.
Is drone insurance necessary?
Drone insurance is highly recommended to protect against liability for accidents or damage caused by your drone. Check your local regulations for mandatory insurance requirements.